n northern regions and elevated areas, snow pack develops in winter months with melting occuring during the summer. The melting snow pack in a watershed is a major source of fresh water that flows into streams and rivers. Drinking, irrigation, recreation and hydro electric power generation are among the critical water uses impacted by snow melt.
Problem
Every year hydrologists must forecase snow melt run-off in key watersheds. How much water should be retained in reserviors and how much allowed to flow out? What is the appropriate way to control the danger of flooding?

GPR Contribution to Solution
Snow is very transparent to GPR signals. Simple GPR reflection surveys are routinely used to map snow thickness. The degree of snow compaction varies resulting in variations in the equivalent water content. This study was focused on demonstrating how GPR velocity measurements could provide snow–to–water content conversion factors.
Snow is very transparent to GPR signals. Simple GPR reflection surveys are routinely used to map snow thickness.
The experimental area was in central Norway. The snow pack was the one that did not melt totally each year and was adjacent to a glacier. Having aged snow provided a larger density contrast in the snow pack.
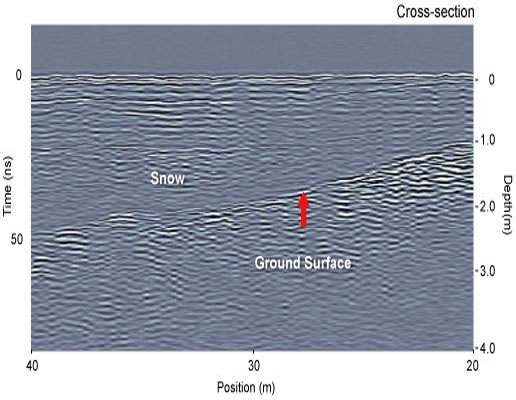
GPR was first used to obtain reflection profiles of a series of test lines. Zones with extended snow layering were sought. Multi-offset CMP measurements were then acquired to enable the estimation of GPR velocity versus depth.
The water volume equivalent of snow can be determined if the snow density is known. Snow can be viewed as a mixture of ice and air with the density being proportional to the volume fraction of ice. Using mixing models that relate the volume fraction of ice to GPR velocity, density can be inferred if GPR velocity is measured.
The data from this study were used to demonstrate this methodology for determining snow water content. Several groups are now incorporating GPR into their hydrology forecasting.
Basin–area snow converage is readily mapped by satellite imagery. Ground truthing, obtained using GPR profiling on controlled lines, provides the third dimension information on snow pack depth, improving snow volume estimations. Where needed, GPR velocity estimation can be used to adjust snow volume to water volume conversion.

Results & benefits
This case stuy provides background on use of GPR for snow pack hydology forecasing. Some key benefits are:
- GPR provides a rapid snow reconnaissance tool
- Systems such as SnowScan® and Noggin® 500 systems enable simple and intuitive field opperation
- Users can be effective with minimal training
- A scientifically-reliable method for snow to water conversions is available
Download the case study: Snow to Water
Learn more about pulseEKKO® GPR
GPR responses vary greatly depending on the target being sought and the host material. GPR response variability can be challenging to new GPR users. When learning about GPR, the best practice is to review several similar case studies to develop an understanding of variability. Check for other insightful information on the resources tab to learn more.
Use Contact Us to reach our Application Specialists who can help you tap into Sensors & Software’s vast array of technical information.








