pulseEKKO®
Borehole GPR
Borehole ground penetrating radar surveys are performed by inserting borehole antennas in open or plastic-cased boreholes as small as 33mm (1.25 inches) in diameter and collecting the signals from the borehole to an adjacent borehole or the surface. Borehole antennas are accessories of a standard low frequency pulseEKKO GPR system. The system utilizes the same transmitter and receiver electronics units as the low frequency surface antennas.
Borehole GPR Applications
- Locate tunnels, cavities, and solution voids
- Map beneath electrically conductive soils that limit surface deployed GPR
- Detect underground storage tanks (USTs) under buildings
- Detect large, buried UXOs in areas where magnetometers cannot be used
- Examine rock mass uniformity
- Locate leaks from USTs
- Examine foundations, piers and piles
- Locate conductive groundwater contamination
- Monitor grout injection
- Monitor environmental remediation such as air sparging
- Measure the physical properties of stratigraphy


Borehole Survey Types
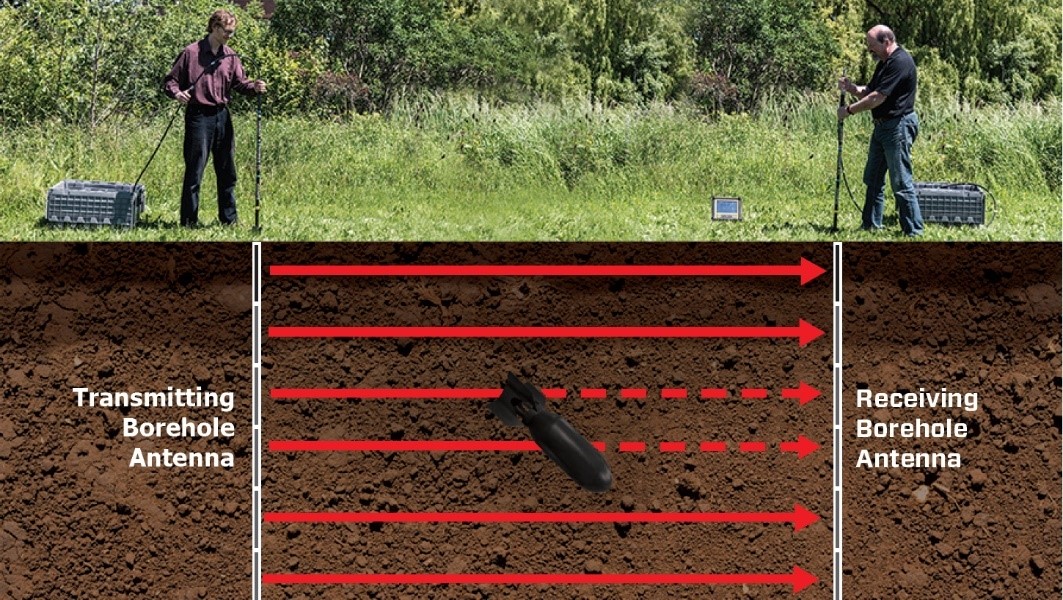
Zero Offset Profile (ZOP)
Quick and simple survey that is easy to interpret. Borehole antennas are moved together equal intervals and the signal between the boreholes is recorded. Variations in signal travel time and amplitude shows changes in material properties between boreholes including the presence of object or tunnels.

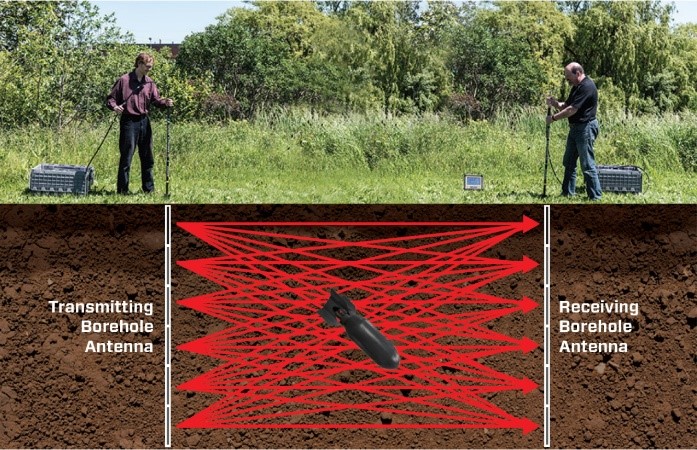
Multiple Offset Gather (MOG)
A MOG is collected by fixing the transmitting antenna at one depth in the borehole while the receiving antenna moves at increments in the other borehole. Each MOG covers a triangular area between the boreholes. Multiple MOGs, each with the transmitting antenna at an incrementing depth are necessary to cover the whole area between the boreholes. Tomographic processing of the data is necessary to create images of the properties between boreholes (software available from third parties).


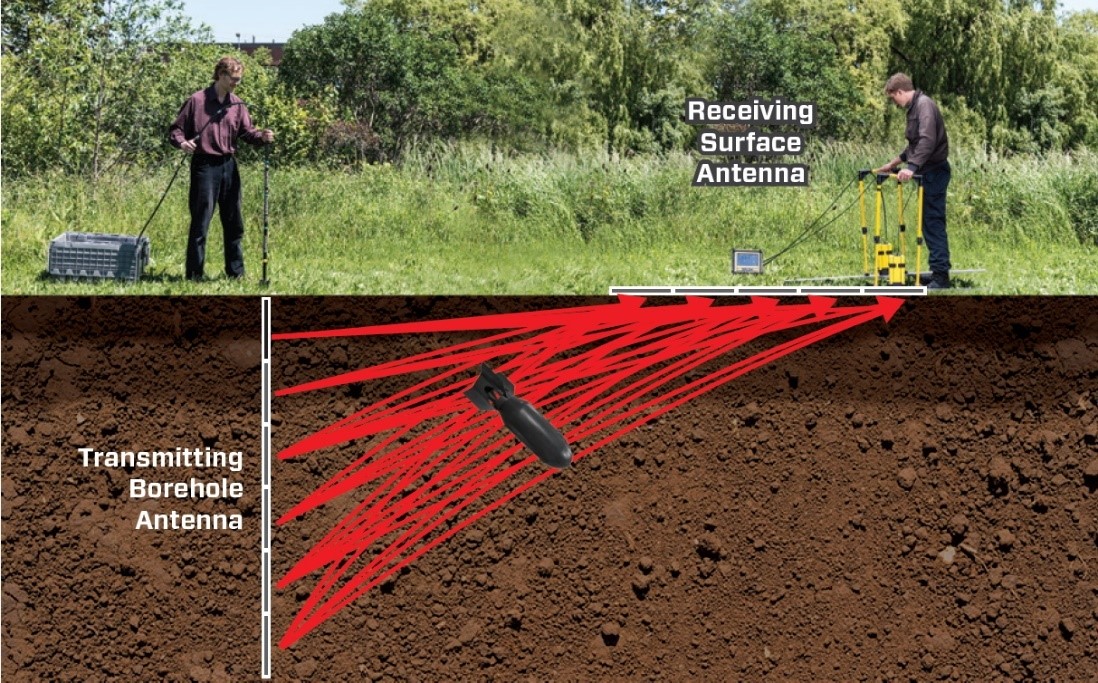
Vertical Radar Profile (VRP)
VRPs record signal from a single borehole to the surface. The transmitting borehole antenna is fixed at a depth and signal is sent to a receiving antenna moving increments across the surface. Multiple VRPs, each with the borehole antenna at an incrementing depth, are necessary to over the whole area. Processed data shows changes in material properties and objects in a wedge between the borehole and surface.

Borehole GPR Features

- Slim diameter, waterproof, fiberglass casing
- 50, 100 and 200 MHz borehole antennas available
- Uses center-fed dipole antennas
- Antenna casing sized to provide consistent antenna center point over all frequencies

- Waterproof, rugged cable connector with strain relief allows quick interchange of antenna elements
- Unique stealth metallic cable system to deliver signals to and from the antennas with minimal external interference

- Cables marked at 0.25m intervals for easy positioning

- Shielded enclosures to house transmitter and receiver and minimize interference
Contact Us
Lease to Own option available







